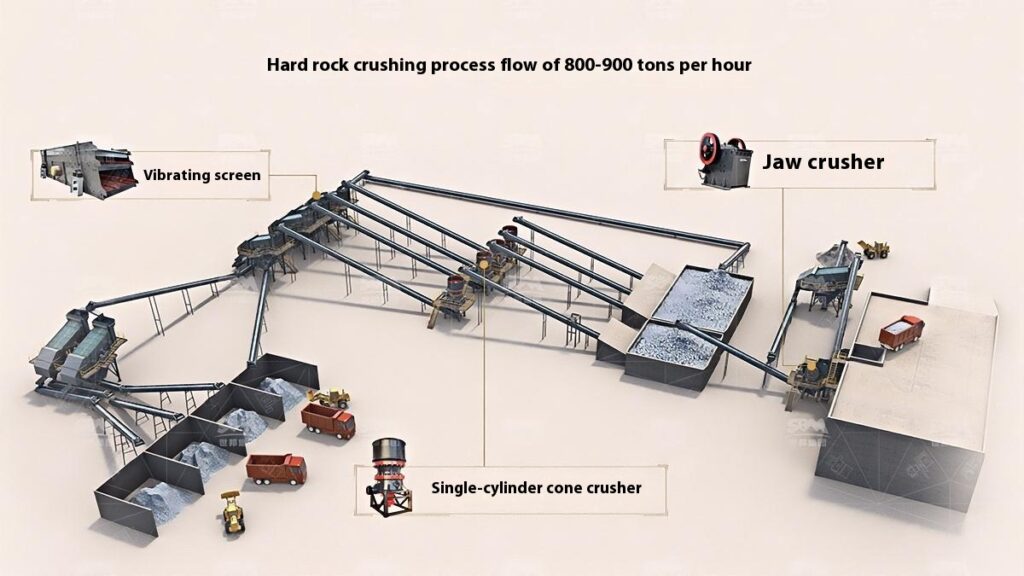
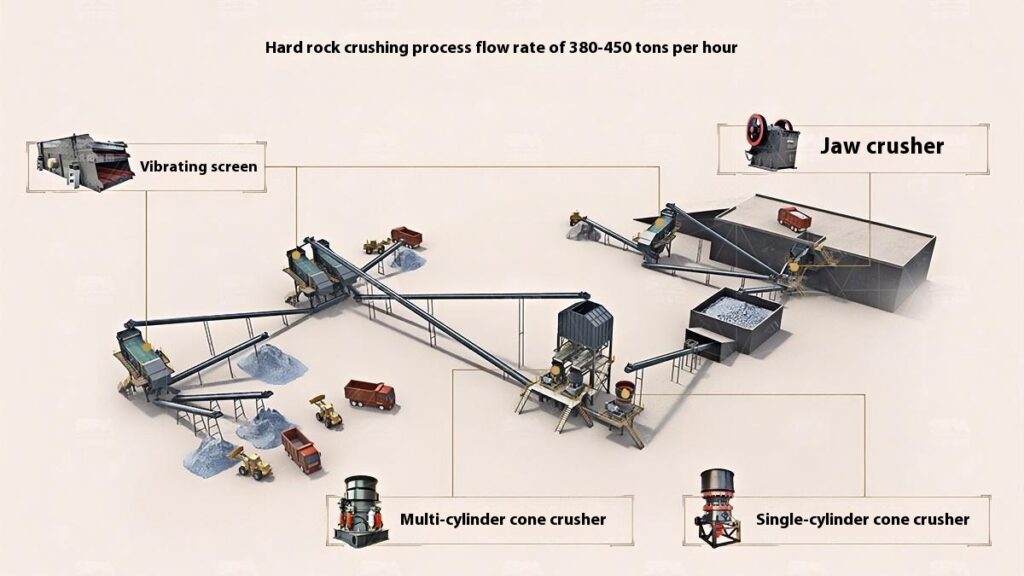
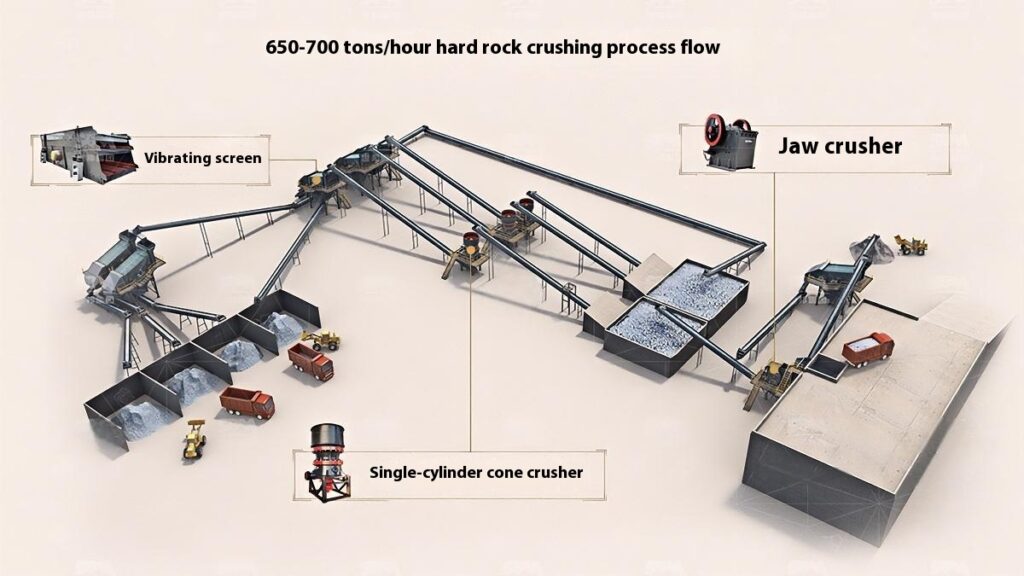
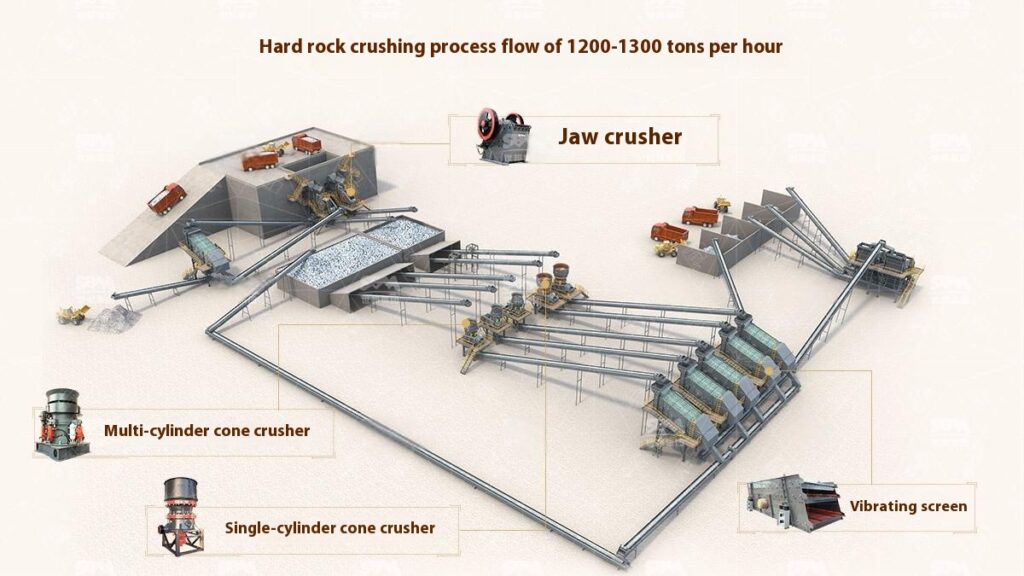
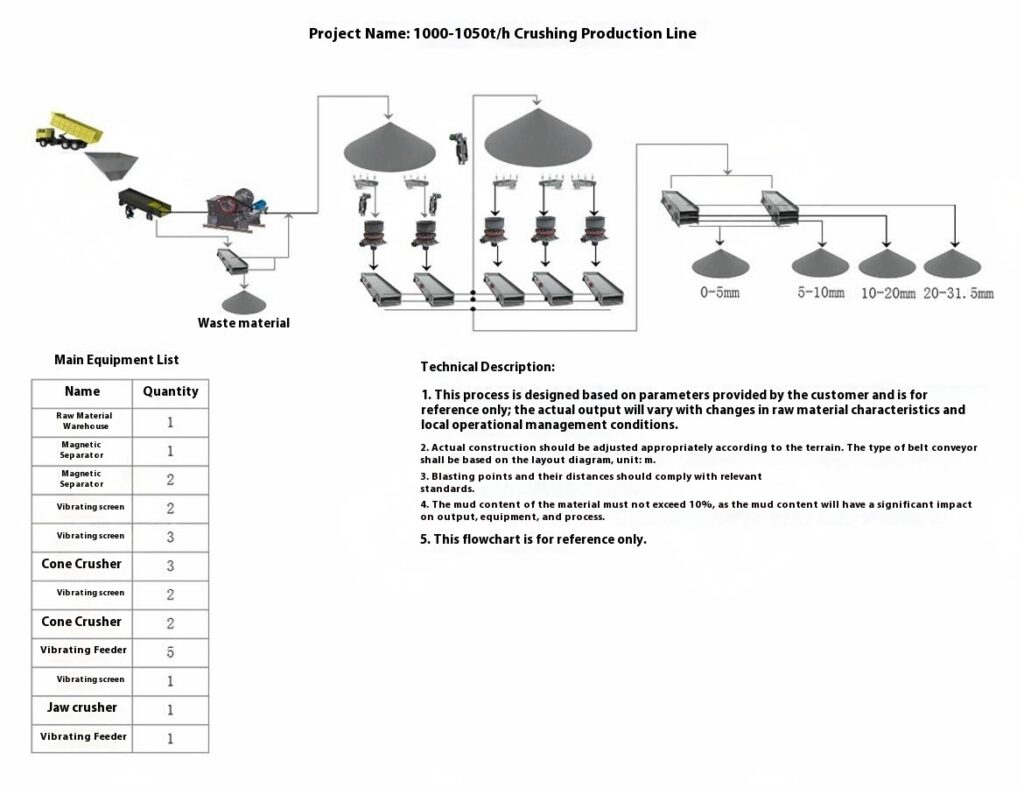
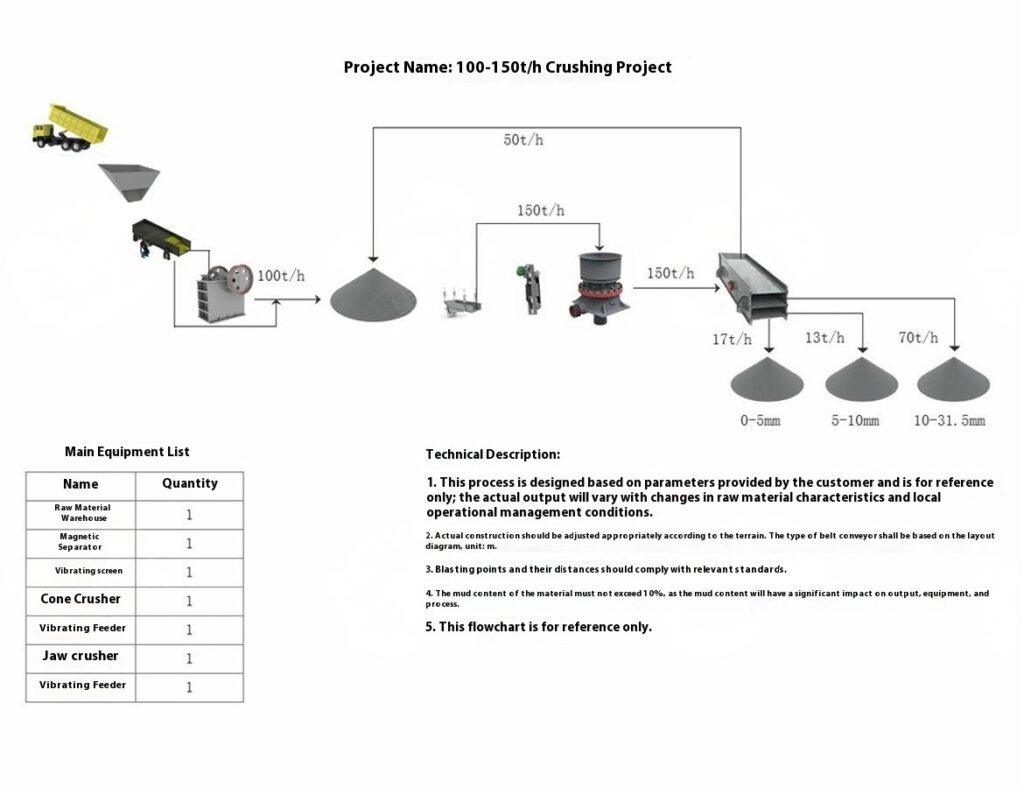
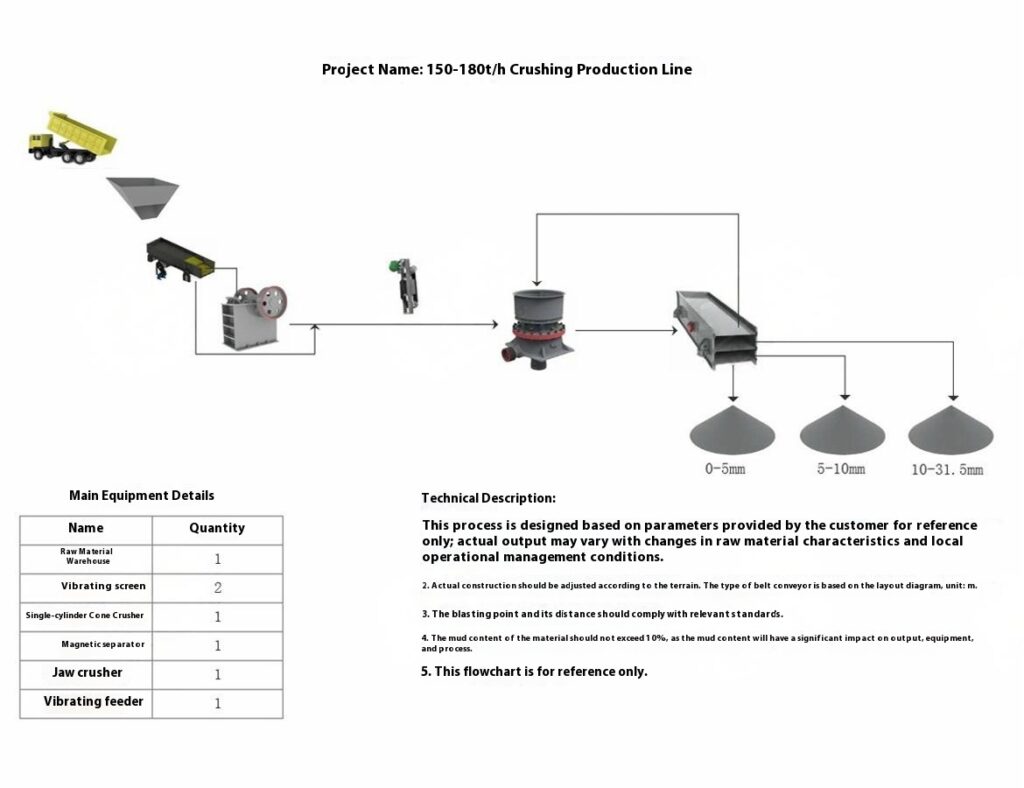
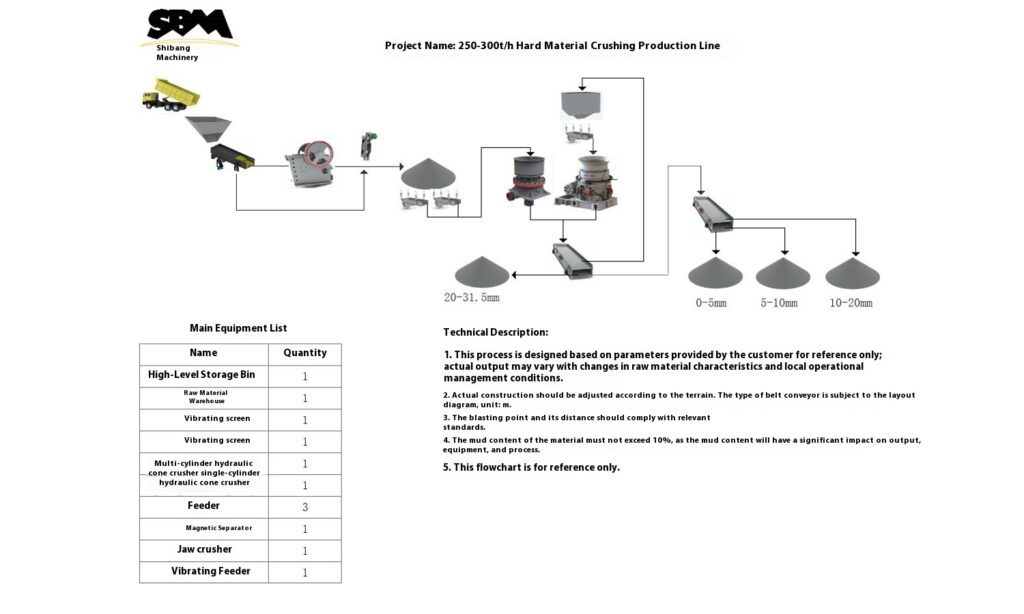
Design Scheme
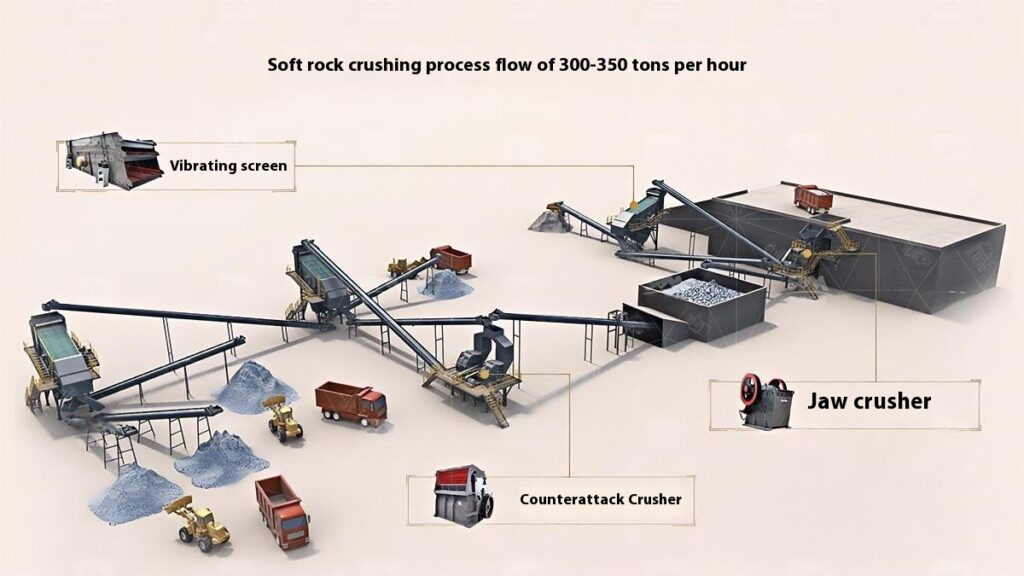
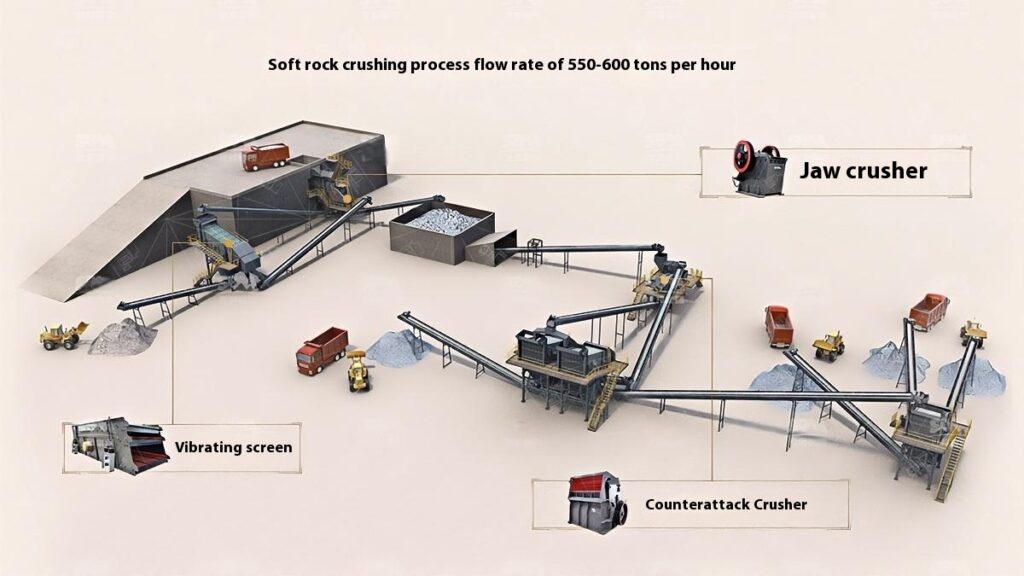
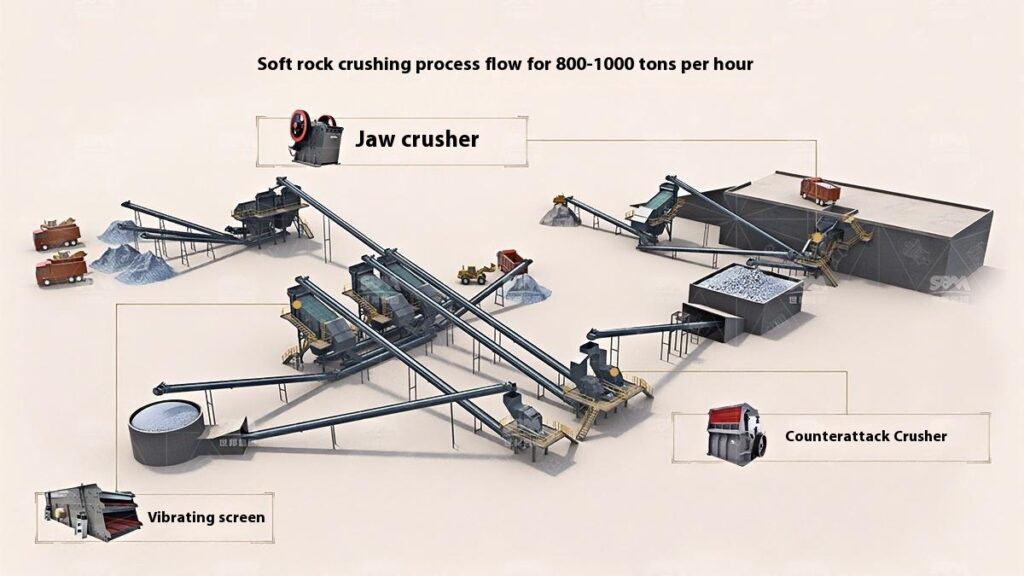
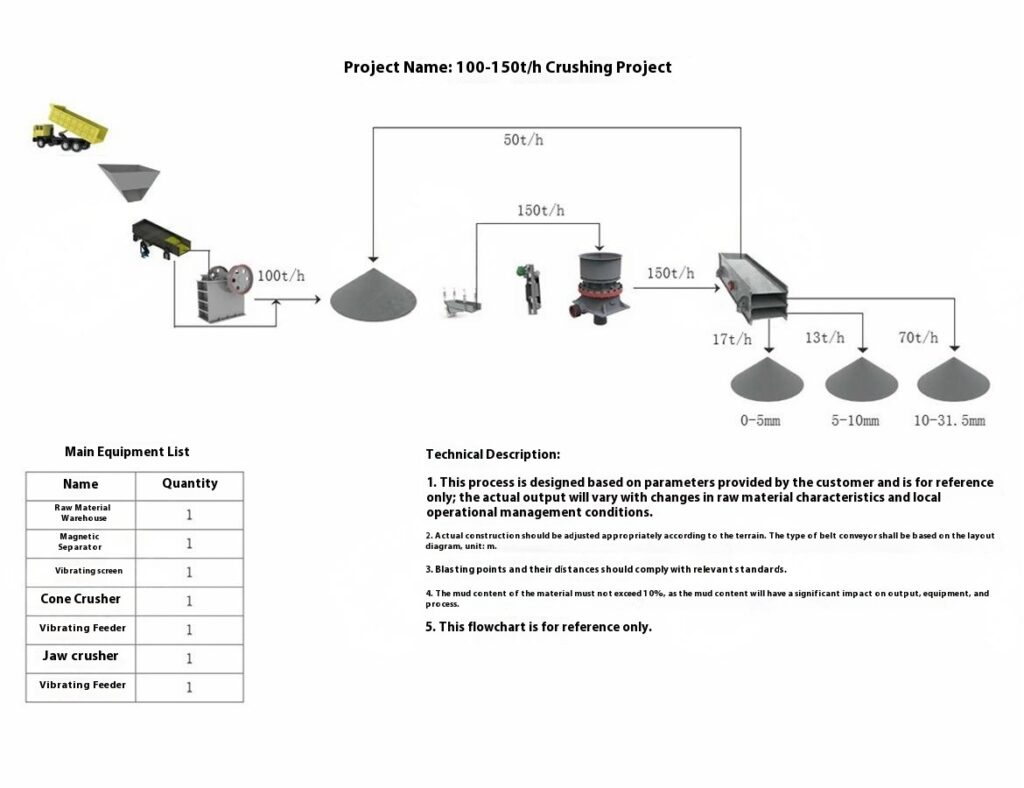
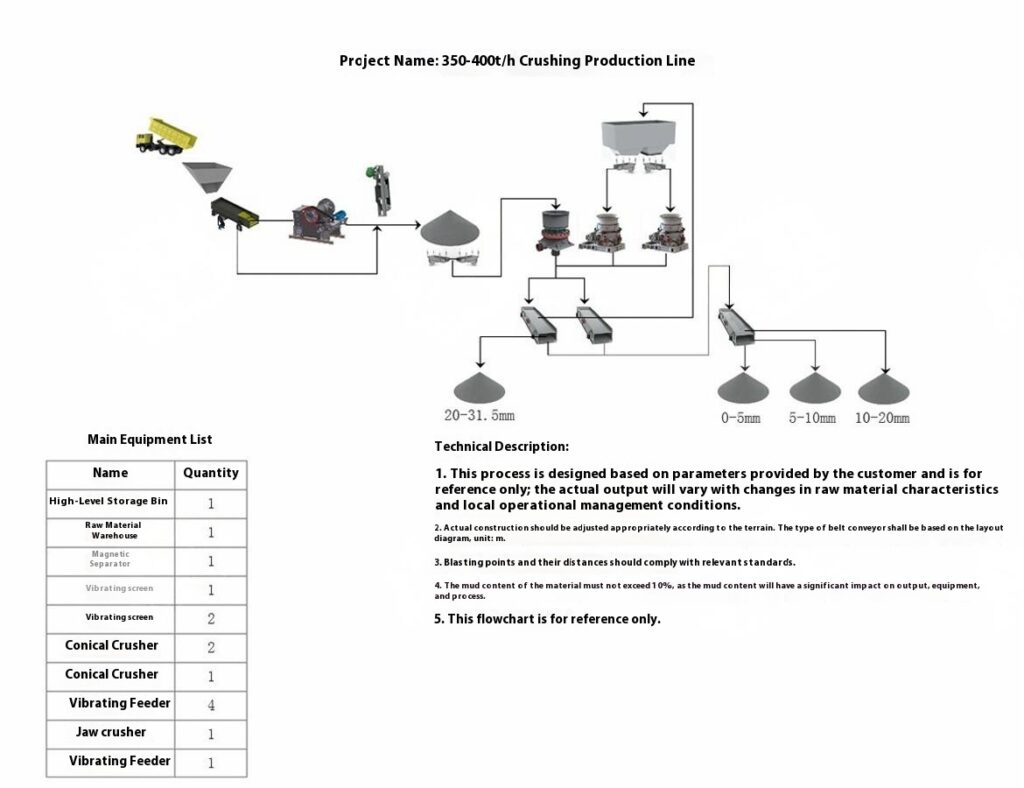
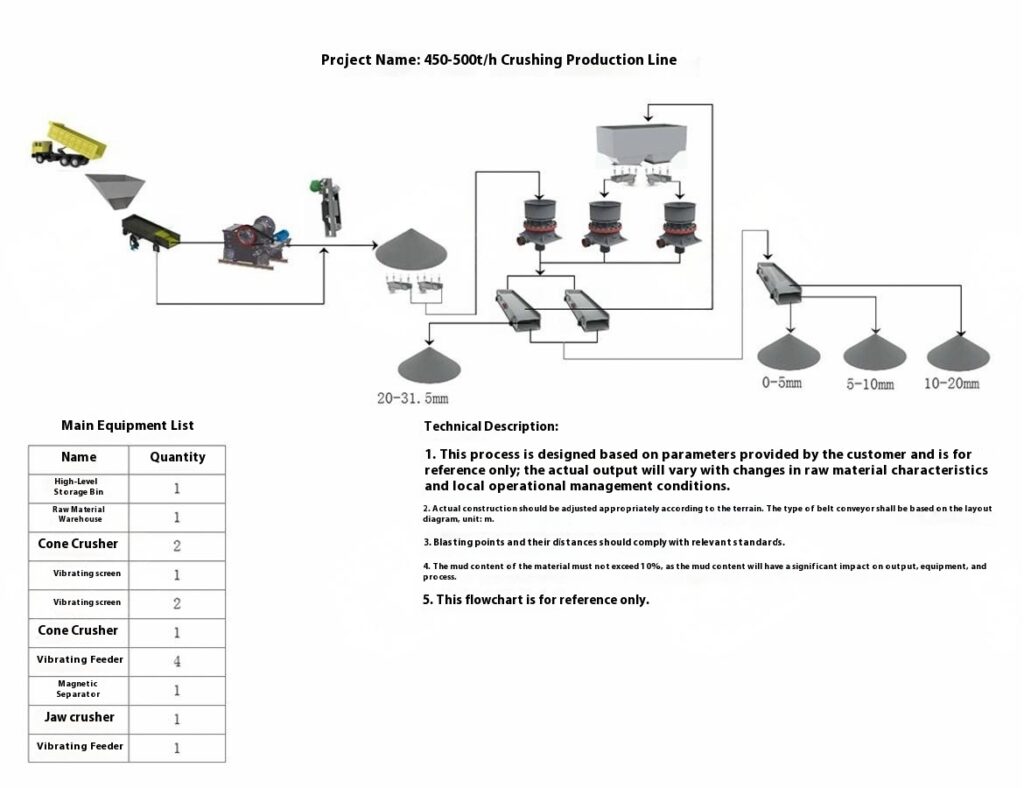
Construction Aggregates Crushing Process
Combined Crushing Process (Applicable to Railway Ballast, Basalt, River Pebble, หินแกรนิต, Feldspar, and Limestone)

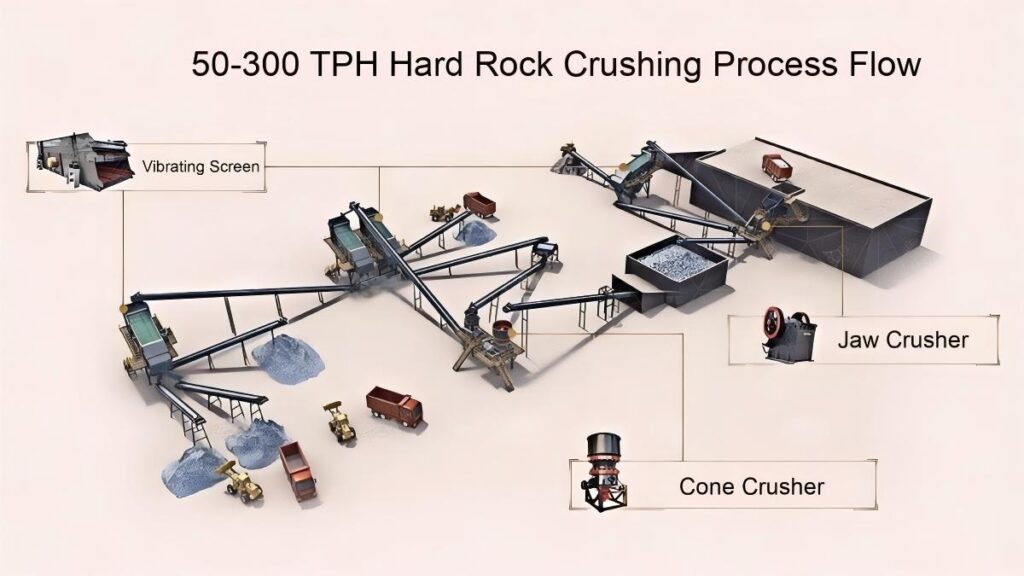
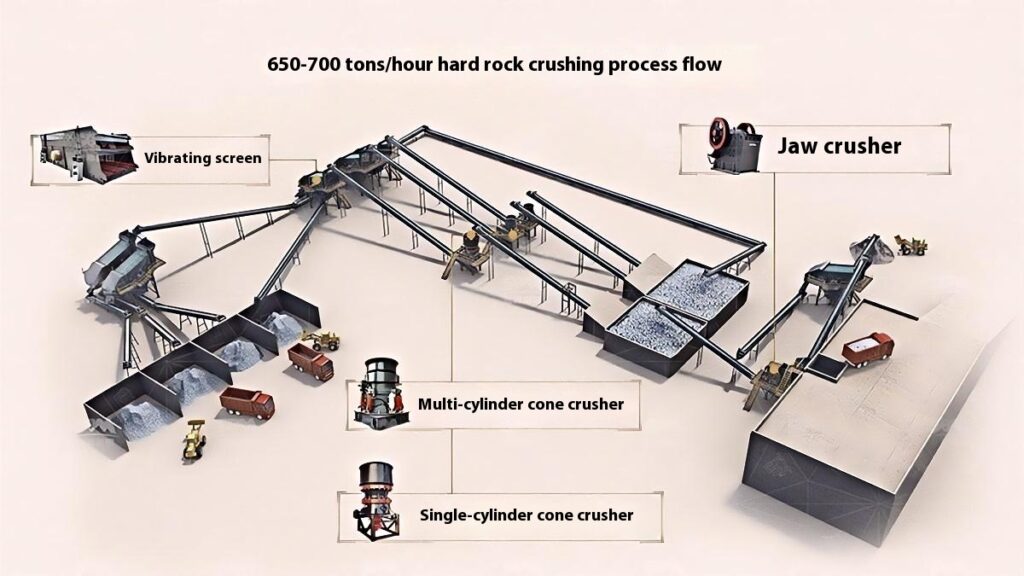
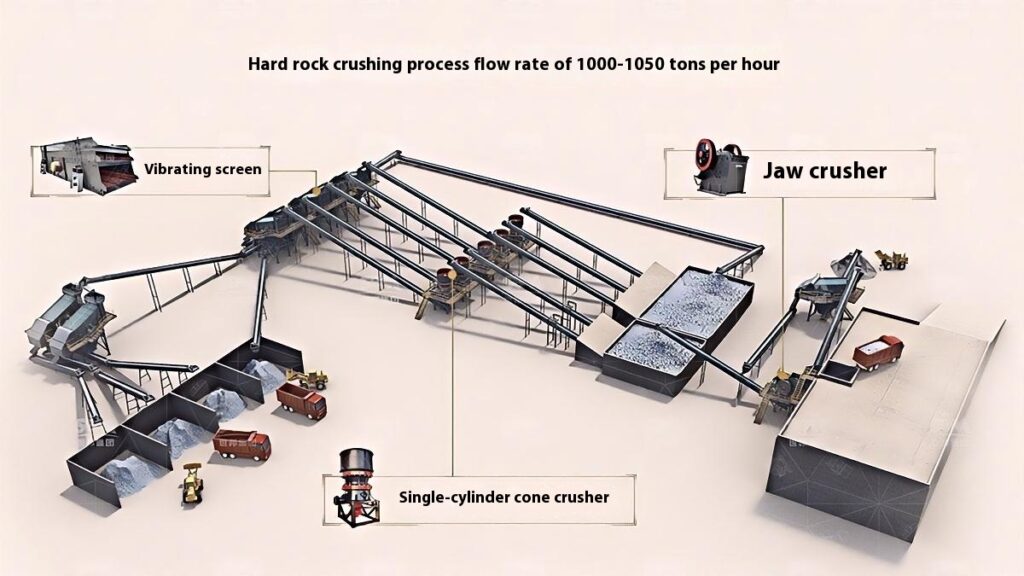
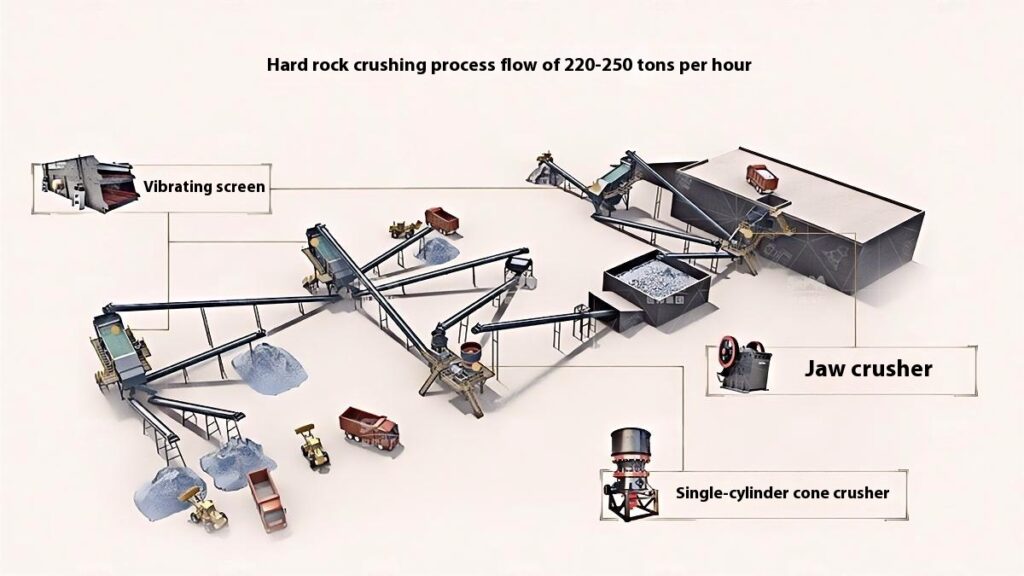
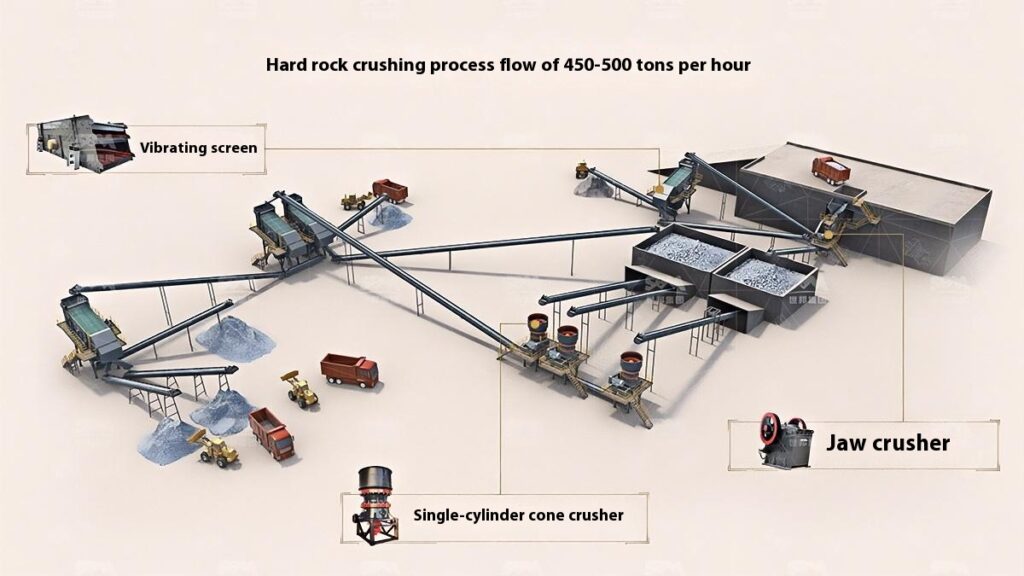
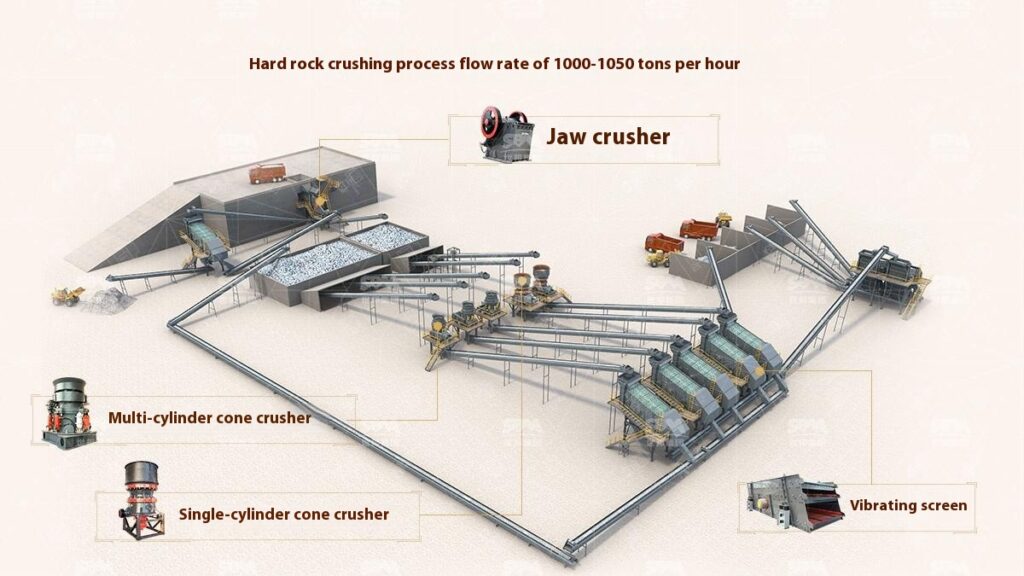
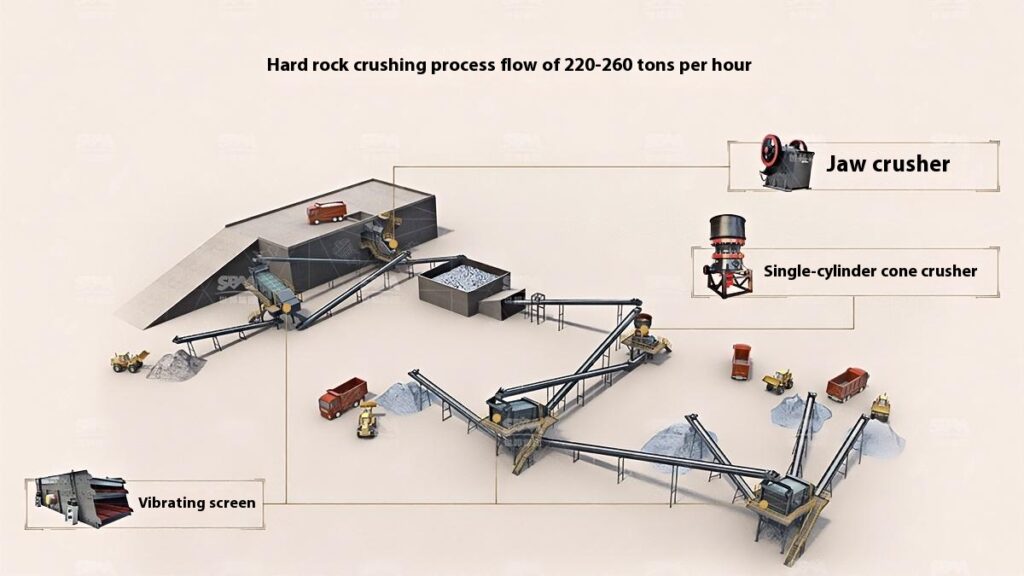
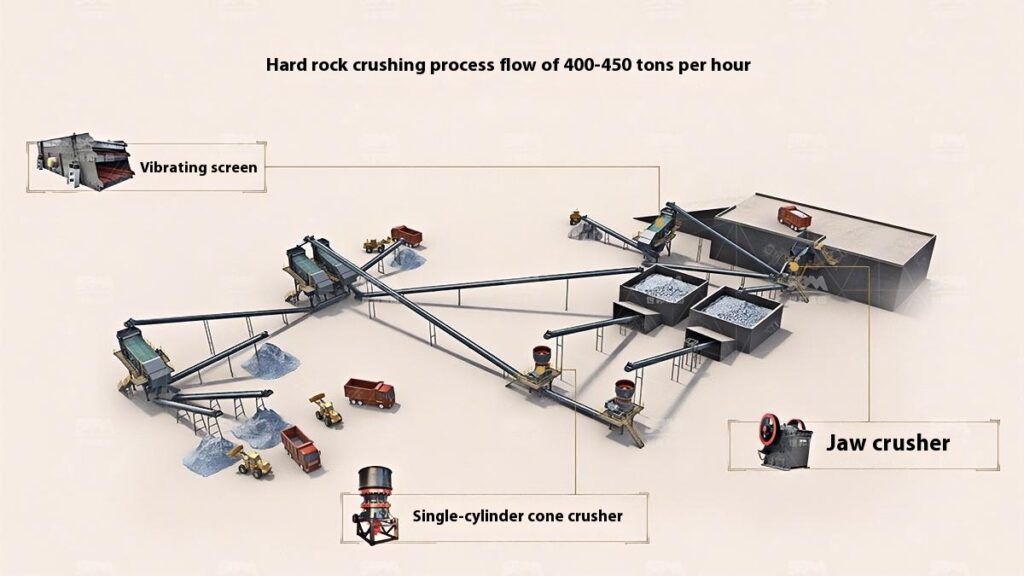
1. Raw Material Preprocessing
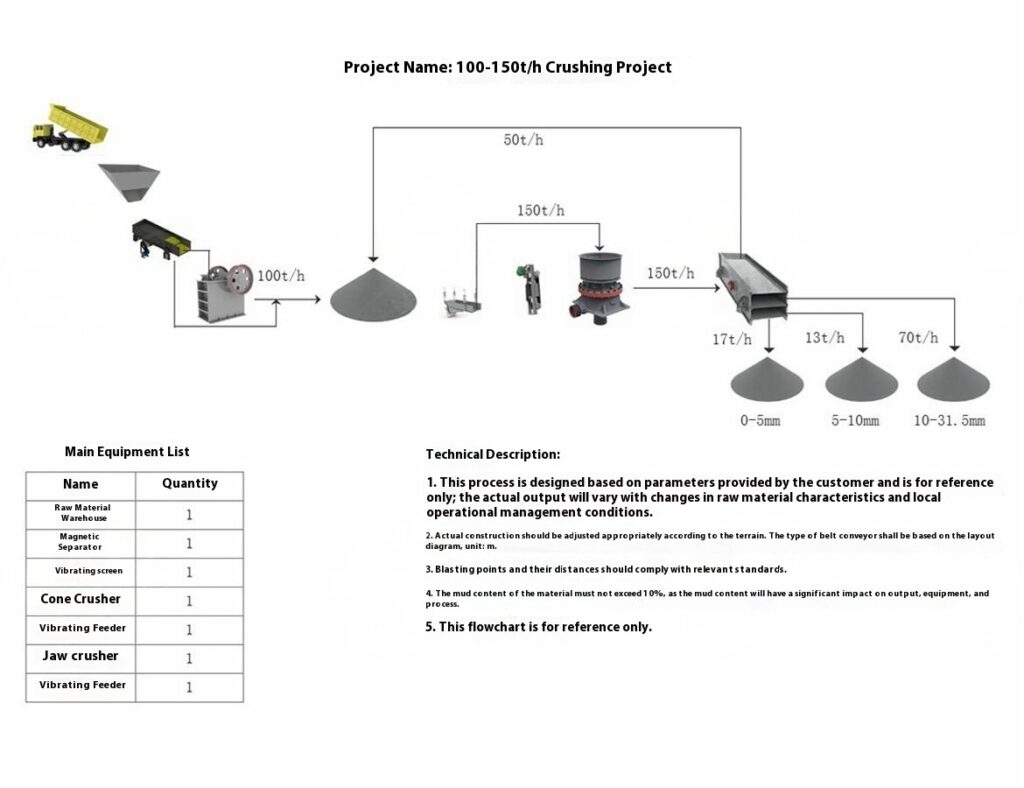
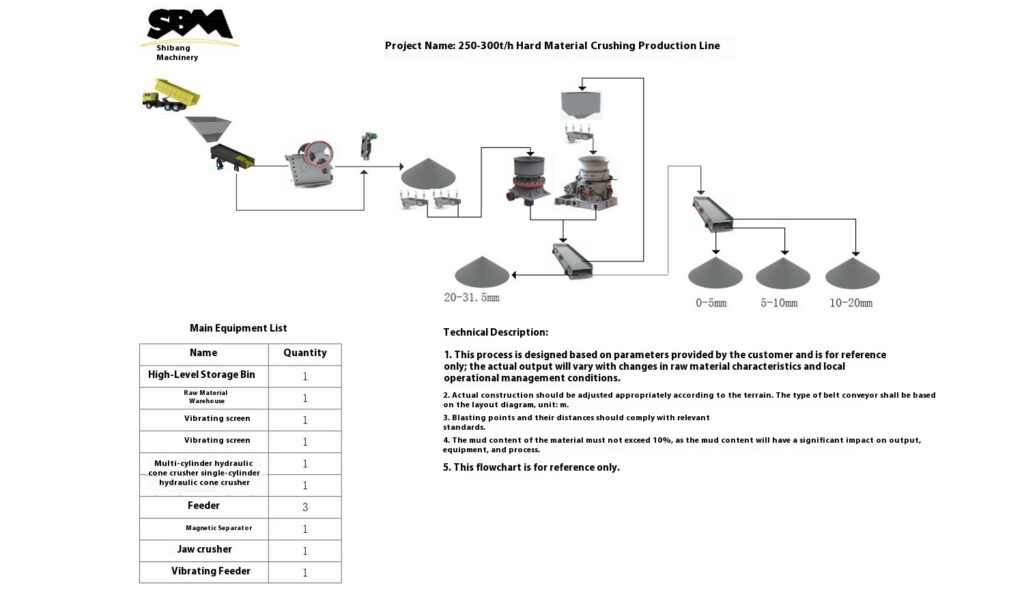
Use a vibrating feeder to ensure uniform feeding, maintaining stable operation of the equipment.
2. Primary Crushing
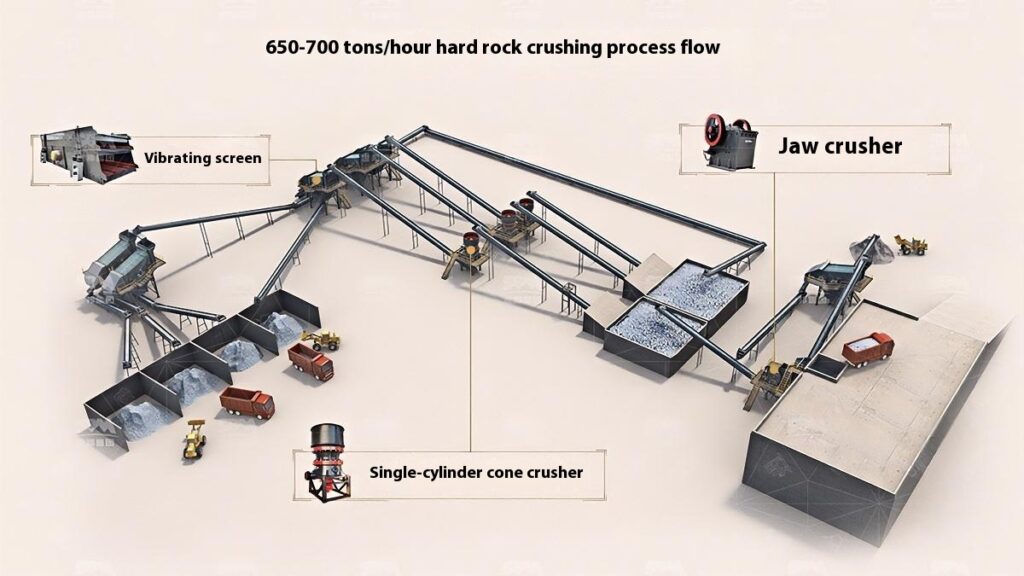
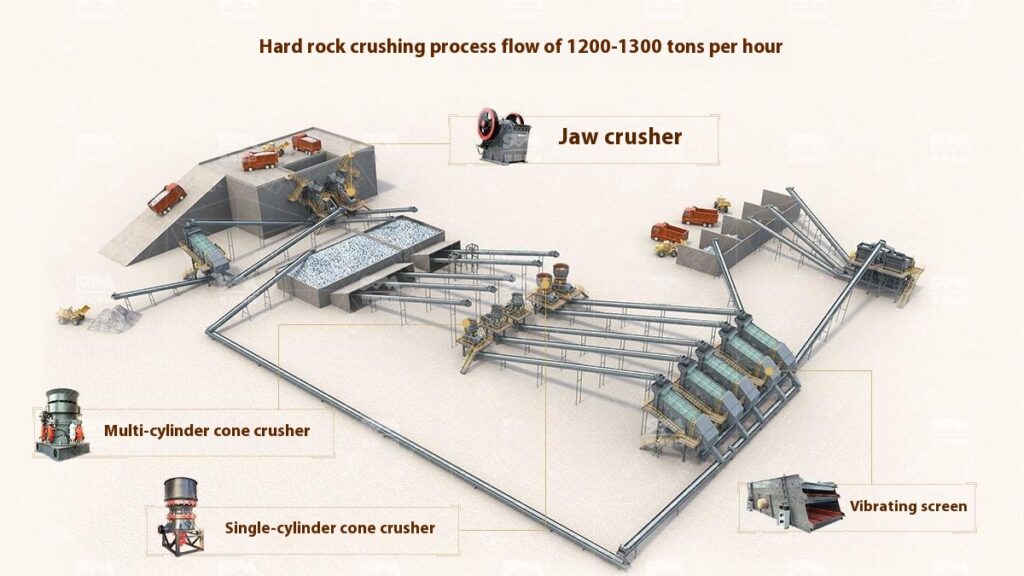
Use a jaw crusher for primary crushing to process large raw materials, achieving initial particle size reduction for subsequent processing.
Applicable to all types of stones for primary crushing.
3. Secondary Crushing
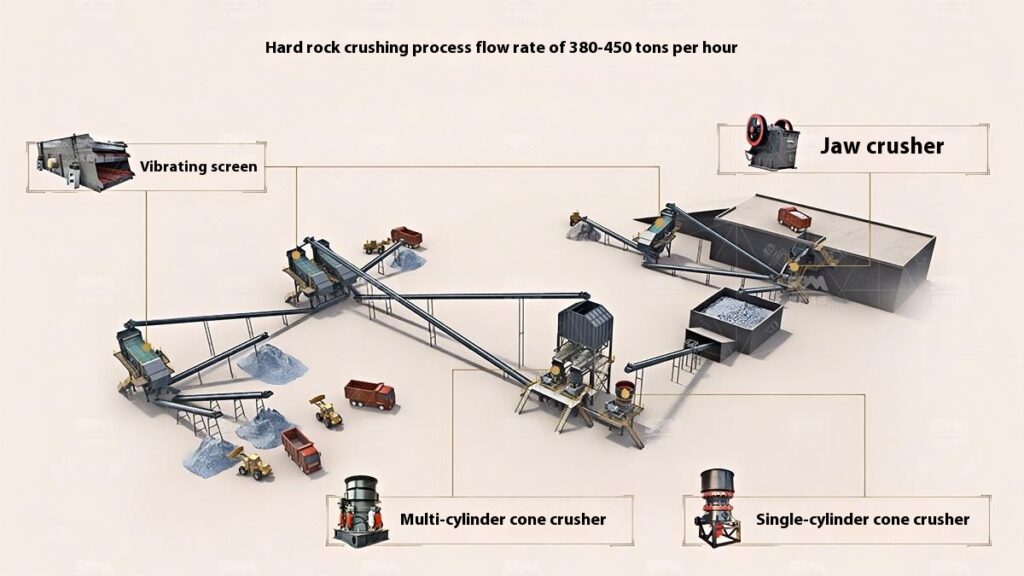
Select cone crusher or impact crusher for secondary crushing based on stone hardness and crushing requirements.
Hard stones such as basalt, granite, and feldspar mostly use cone crushers.
Softer stones or those requiring shaping, like railway ballast, river pebble, and limestone, mainly use impact crushers.
4. Screening and Classification
Use vibrating screens to classify the crushed materials, separating qualified products that meet the particle size requirements.
Unqualified materials are returned to the crusher for reprocessing to ensure consistent product quality.
5. Finished Product Stacking
Stack qualified finished products according to particle size specifications for easy transportation and further use.
Process Key Points
Ensure uniform feeding to avoid equipment blockage or overload.
Select appropriate crushing equipment to guarantee crushing efficiency and product quality.
Strictly control particle size during screening to ensure the shape and size of stone materials meet standards.
For hard stones such as basalt and granite, pay attention to equipment wear resistance.
Basalt
High hardness, dense structure, high compressive strength
Chemically stable, resistant to weathering
Typically dark gray or black in color
Basalt Crushing Process:
Raw material feeding → Primary crushing (jaw crusher) → Secondary crushing (cone crusher) → Vibrating screening and classification → Finished product stockpiling
Railway Ballast
High hardness and excellent wear resistance
Angular particle shape, ideal for stabilizing railway tracks
High compressive strength and good freeze-thaw resistance
Railway Ballast Crushing Process:
Feeding → Primary crushing (jaw crusher) → Secondary crushing (impact crusher or cone crusher) → Vibrating screening → Selection of products with required particle size → Oversized materials returned for re-crushing
Feldspar
High hardness, brittle nature
Dense structure with stable chemical properties
Available in various colors, commonly white, pink, or gray
Feldspar Crushing Process:
Feeding → Primary crushing (jaw crusher) → Secondary crushing (cone crusher or impact crusher) → Vibrating screening and classification → Finished product stockpiling
หินแกรนิต
Dense structure, high hardness, excellent wear resistance
Various colors, commonly gray, pink, or red
High compressive strength and strong weather resistance
Granite Crushing Process:
Feeding → Primary crushing (jaw crusher) → Secondary crushing (cone crusher or impact crusher) → Vibrating screening → Product classification
หินแกรนิต
Dense structure, high hardness, excellent wear resistance
Various colors, commonly gray, pink, or red
High compressive strength and strong weather resistance
Granite Crushing Process:
Feeding → Primary crushing (jaw crusher) → Secondary crushing (cone crusher or impact crusher) → Vibrating screening → Product classification
Limestone
Relatively soft texture with low hardness
Contains calcium carbonate, easily eroded by acidic substances
Typically light gray, white, or yellow with uniform texture
Limestone Crushing Process:
Feeding → Primary crushing (jaw crusher) → Secondary crushing (impact crusher) → Vibrating screening → Product classification → Oversized materials returned for re-crushing
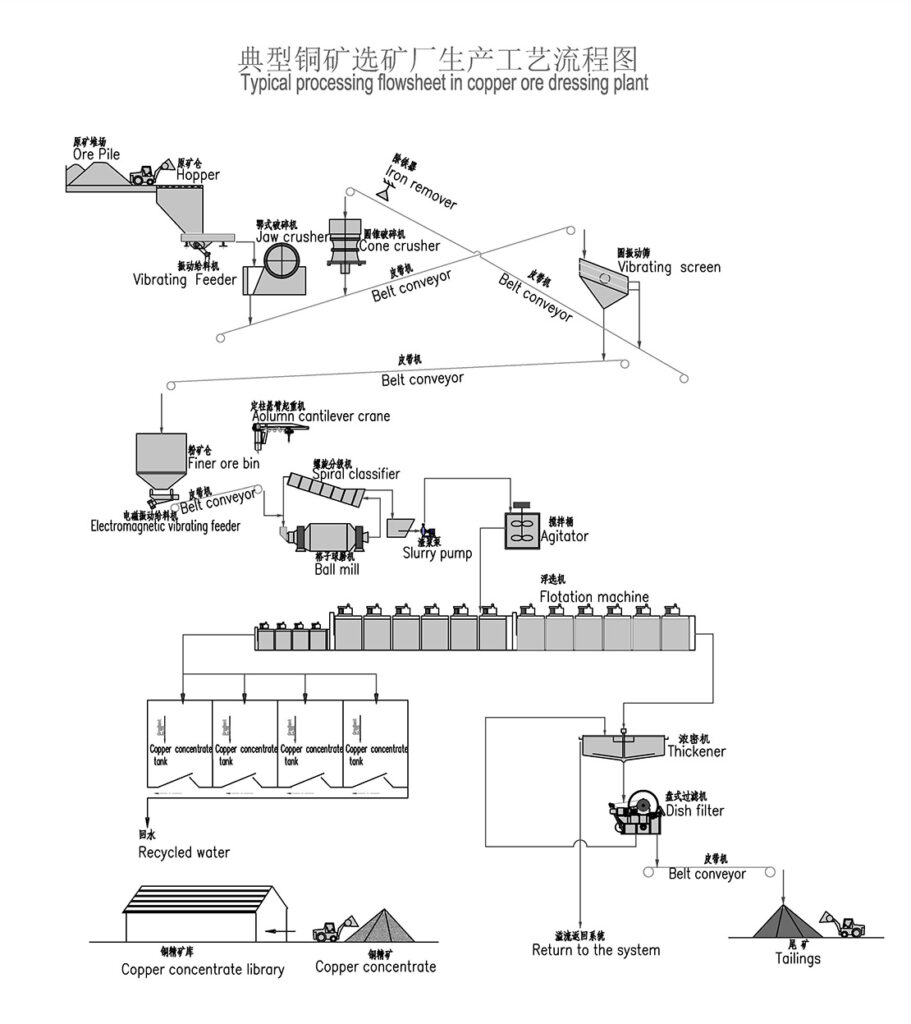
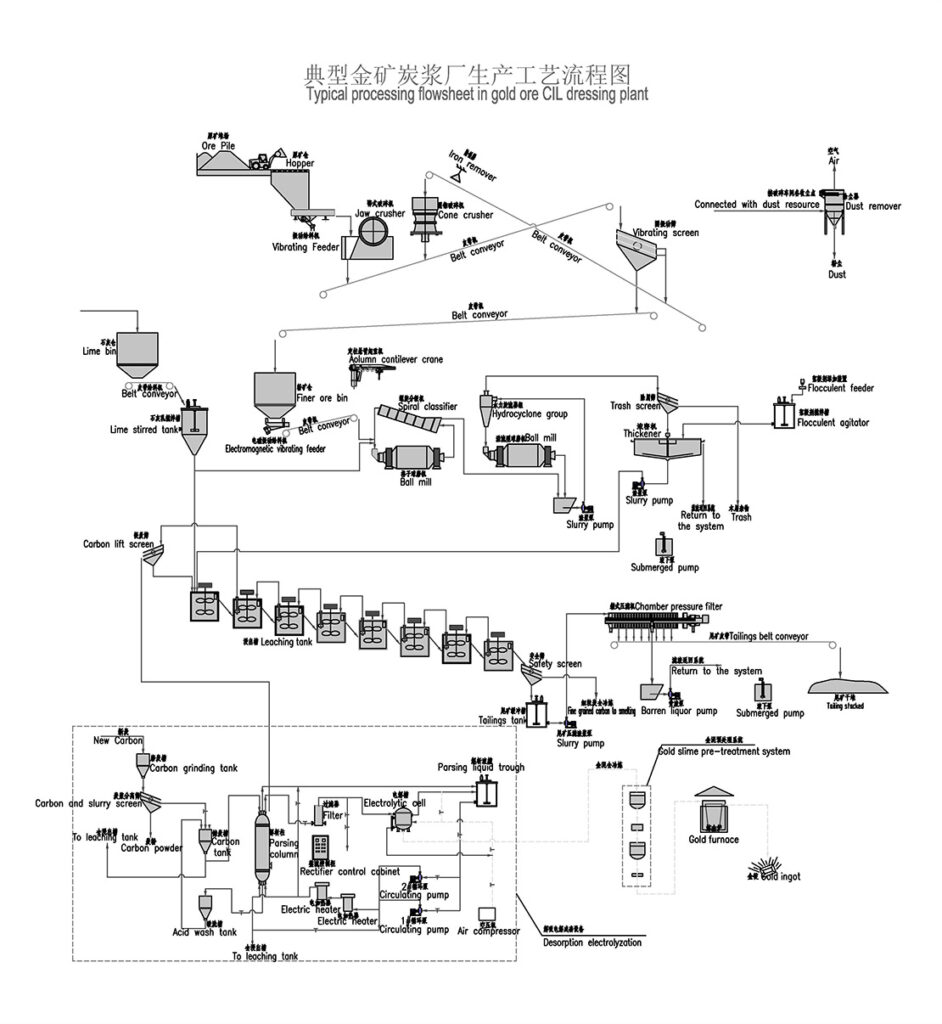
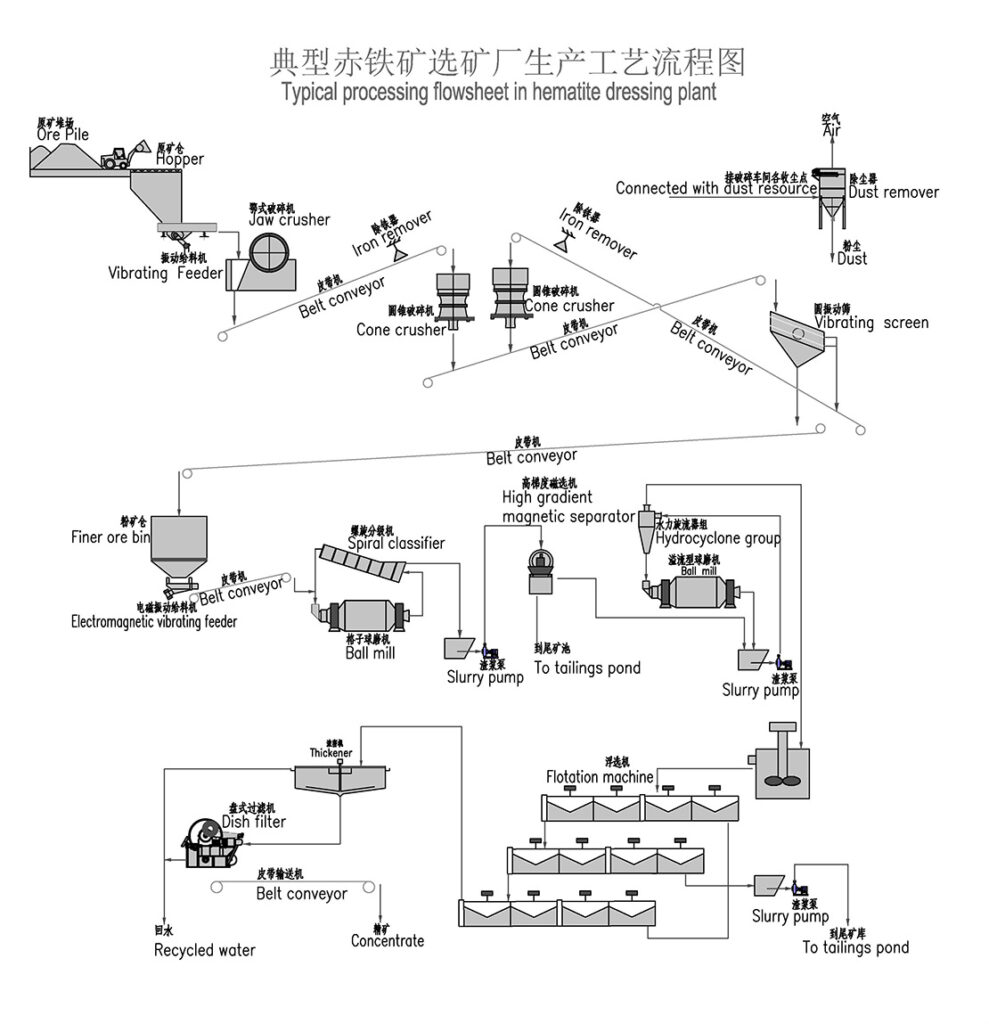
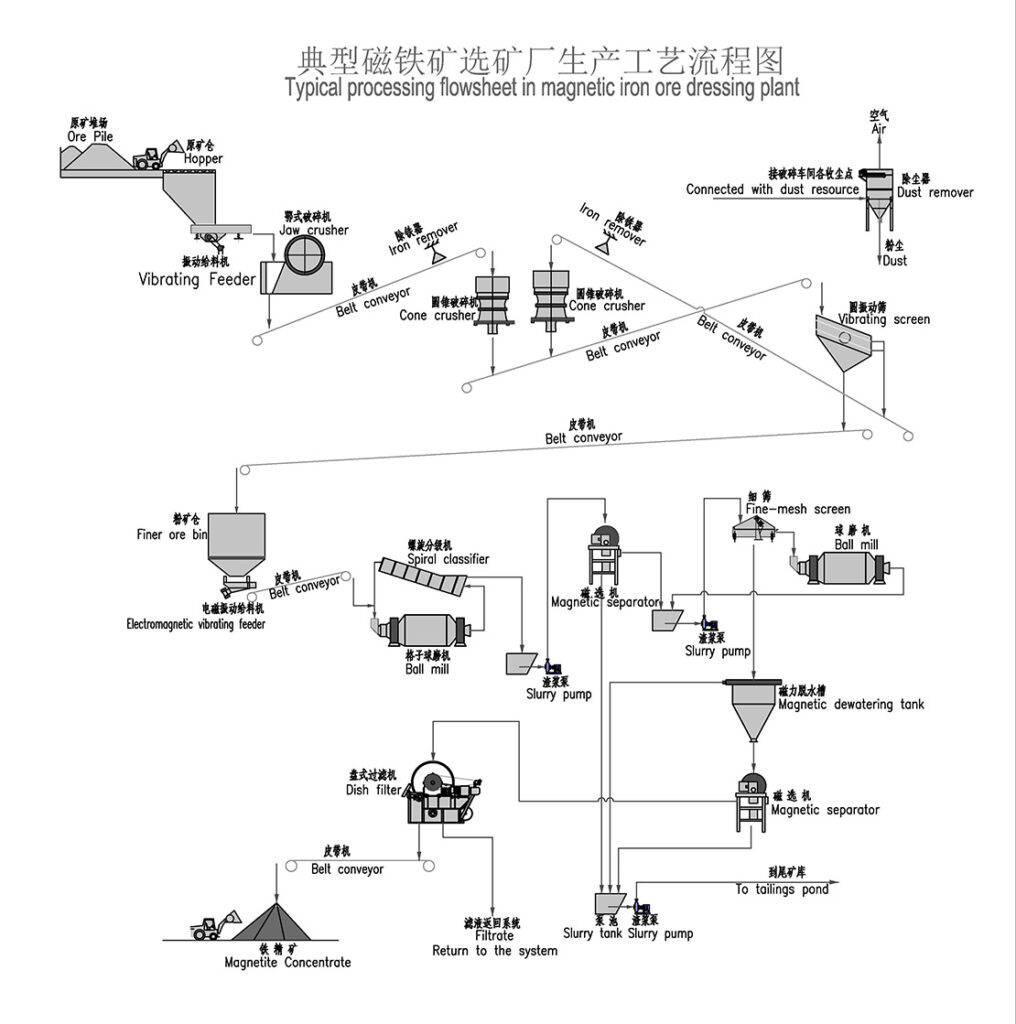
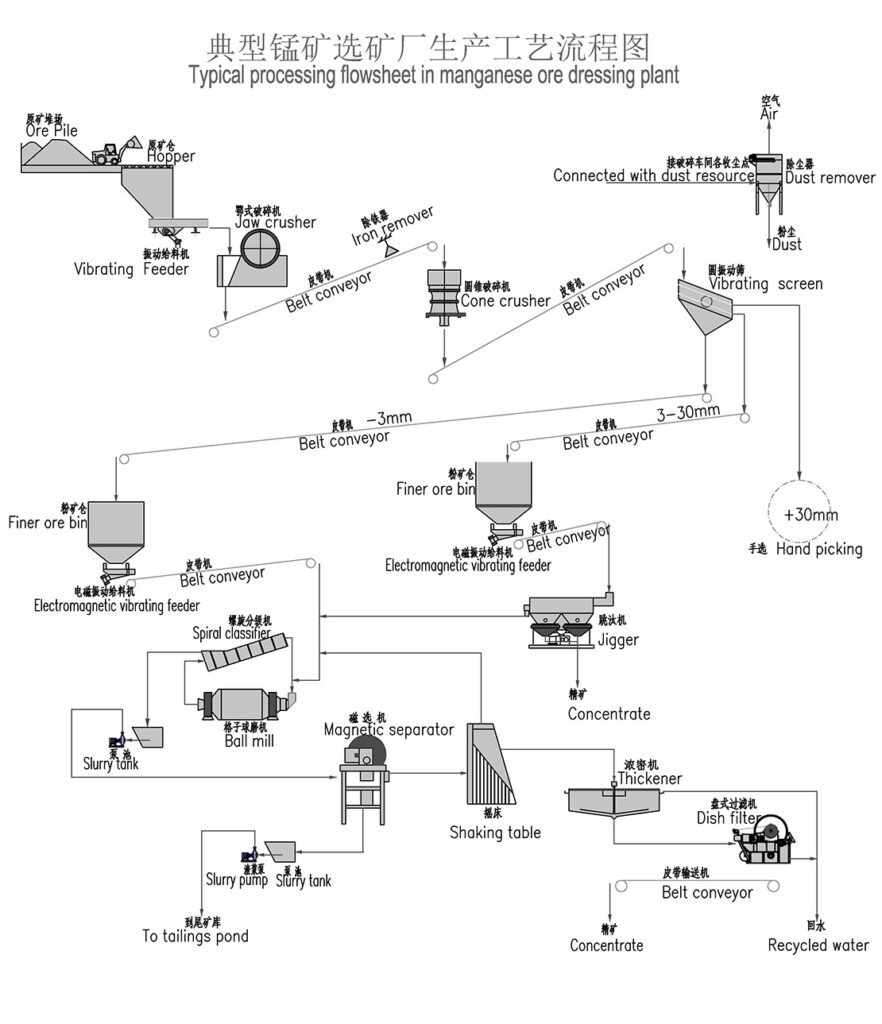
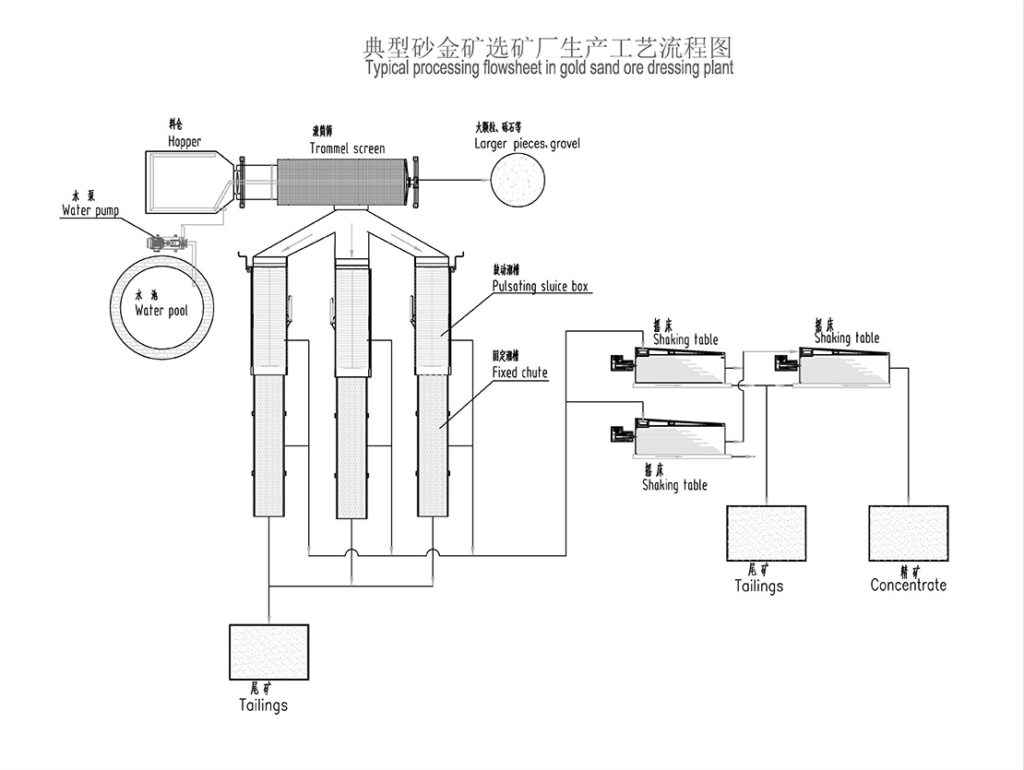
Non-Ferrous Metal Ore Crushing Process
Combined Crushing Process for Various Metal Ores
This combined crushing process is suitable for a variety of metal ores including hematite , manganese ore , magnetite , placer gold , gold ore , iron ore , copper ore , and copper ore rock .

1. Raw Material Feeding
Use vibrating feeders to ensure uniform, continuous feeding of ore materials into the crushing system for stable operation.
2. Primary Crushing
Large ore blocks are reduced in size by jaw crushers to facilitate further processing.
3. Secondary Crushing
Based on ore hardness and particle size requirements, cone crushers or impact crushers are employed for secondary crushing.
Hard ores like hematite, magnetite, and copper ores often use cone crushers.
Softer ores such as placer gold and some manganese ores may use impact crushers.
4. Screening and Classification
Vibrating screens classify crushed ore into different particle size ranges.
Oversized material is returned to crushers for further reduction, ensuring uniform product size.
5. Finished Product Stockpiling
Qualified crushed ore products are stockpiled by size for transport or further processing.
Process Highlights
Ensure uniform feeding to avoid equipment overload or blockage.
Select appropriate crushers based on the ore’s hardness and abrasiveness.
Maintain strict control on particle size through screening to ensure product quality.
Use wear-resistant equipment components to handle the abrasive nature of metal ores, improving equipment life.