Crushing Equipment — Cone Crusher
I. Working Principle
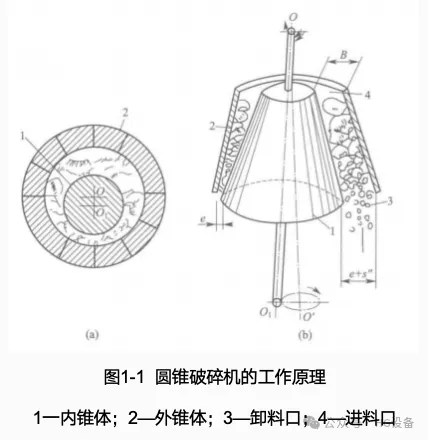
The main working components of a cone crusher are two truncated cones: the inner cone (moving cone) and the outer cone (fixed cone). The fixed cone is connected to the frame by bolts and remains stationary, while the moving cone is mounted on the eccentric shaft and performs a gyratory motion as the eccentric sleeve rotates.
When the moving cone rotates eccentrically along the inner surface of the fixed cone, the material is subjected to compression and bending between the two cones and is crushed. As the moving cone approaches the fixed cone, the gap narrows and the material is compressed and broken. On the opposite side, the gap widens, allowing the crushed material to be discharged by gravity, while the remaining material continues to be compressed until it reaches the discharge size.
During this process, due to the frictional force generated on the surface of the moving cone, the moving cone not only performs eccentric rotation but also rotates in the opposite direction. This additional motion helps produce more uniform product size and ensures even wear on the moving cone surface. The entire crushing and discharging process is continuous, giving the cone crusher greater production capacity and lower energy consumption compared to a jaw crusher.
II. Types and Structures
Cone crushers can be classified according to application and structural design:
- By application
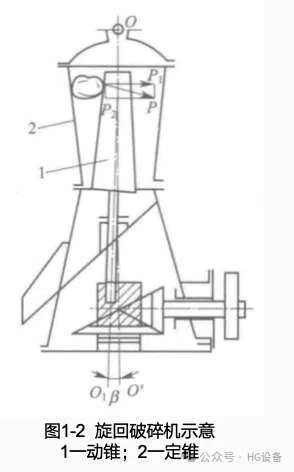
- Coarse crushing cone crusher (gyratory crusher): Used for processing large feed sizes, requiring a wide feed opening. The moving cone is upright, while the fixed cone is inverted.
- Medium and fine crushing cone crusher (mushroom-type crusher): Used for secondary or tertiary crushing. Feed size requirements are smaller, but a wider discharge range is necessary to improve capacity and achieve uniform particle size. In this type, both moving and fixed cones are upright. The moving cone is mushroom-shaped, forming a parallel zone near the discharge port to ensure uniform discharge.
- By structural design
- Suspended-shaft cone crusher (gyratory crusher): Since the vertical component of the reaction force is relatively small, the moving cone can be supported by a suspension device located at the top of the crusher. This design is simple and easy to maintain.
- Mushroom-type cone crusher: Here, the vertical reaction force is larger, so the moving cone is supported from below by a spherical seat. The large support area helps reduce pressure, but since the support is located beneath the crushing chamber, the area is prone to dust and requires effective dust-proofing. This makes the structure more complex and maintenance more difficult.
III. Conclusion
Cone crushers are widely used due to their continuous operation, high capacity, and low energy consumption. Different types and structures serve different production needs: gyratory crushers are suitable for coarse crushing, while mushroom-type cone crushers are more suitable for medium and fine crushing. Proper selection and maintenance of equipment are essential to ensure production efficiency and product quality.

