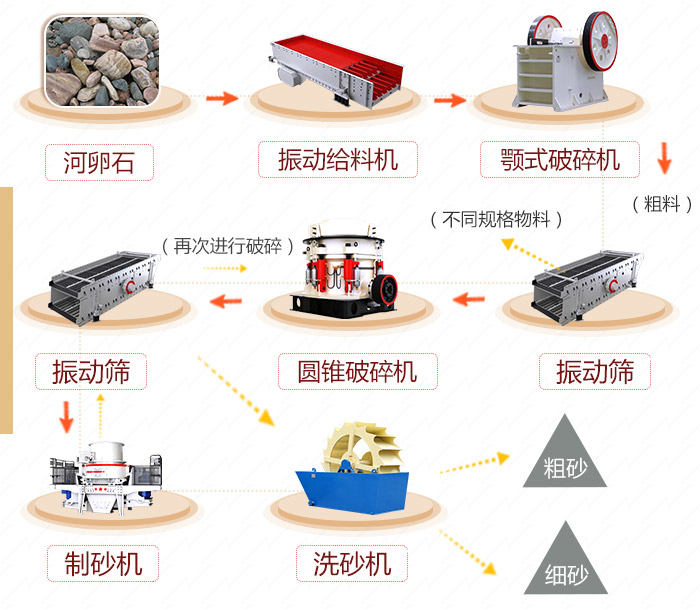
What Are the Common Types of Crushing Machines?
1. Jaw Crusher
Overview:
The jaw crusher uses two jaw plates to crush materials through compression and bending. It is widely applied for primary and secondary crushing of various hardness levels, especially in mining, building materials, silicate, and ceramics industries.
Principio de trabajo:
A fixed jaw plate and a movable jaw plate form the crushing chamber. When the two plates move closer, materials are crushed; when they move apart, smaller particles fall through the discharge opening. The crushing action is intermittent, making it ideal for tough and abrasive materials.
Types:
- Double Toggle Jaw Crusher: Simple arc swing motion.
- Single Toggle Jaw Crusher: Combines arc swing with vertical movement for better discharge and higher efficiency.
Advantages:
- Simple structure, reliable operation
- Capable of handling hard materials
- Adjustable discharge opening
2. Gyratory Crusher
Overview:
A gyratory crusher uses a gyrating cone inside a concave surface to apply compression, splitting, and bending forces to break large rocks. It is primarily used for coarse crushing of all hardness levels of ores and rocks.
Características clave:
- Continuous crushing action, resulting in higher efficiency than jaw crushers.
- Capable of handling feed sizes up to 2000 mm.
Adjustment & Safety:
- Mechanical Adjustment: Using an adjustment nut to raise or lower the crushing cone.
- Hydraulic Adjustment: Using a hydraulic cylinder and accumulator for overload protection and quick discharge opening changes.
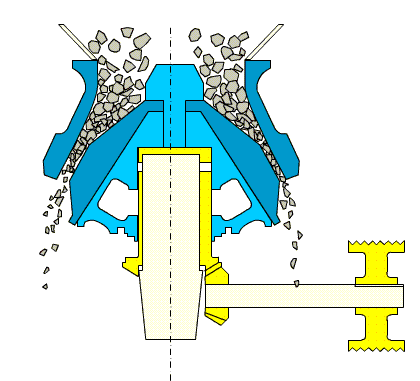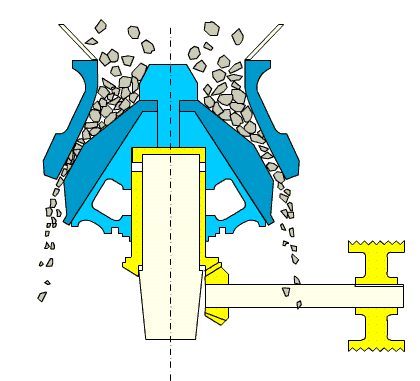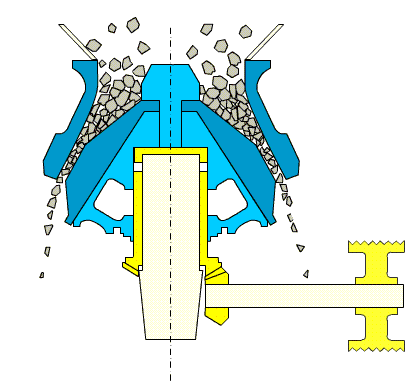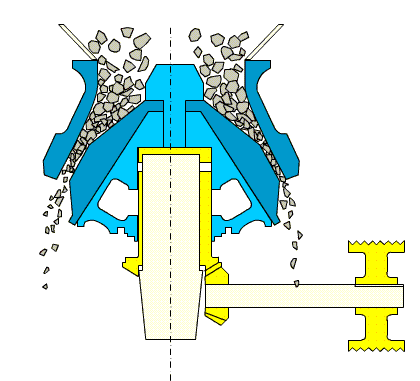
3. Cone Crusher
Overview:
Cone crushers share the same working principle as gyratory crushers but are designed for medium and fine crushing operations. They feature a parallel zone in the lower part of the crushing chamber for uniform particle size distribution.
Types:
- Spring Cone Crusher: Uses springs for overload protection.
- Hydraulic Cone Crusher: Offers precise adjustment and advanced overload safety, similar to hydraulic gyratory crushers.
Advantages:
- High crushing ratio
- Consistent product shape
- Suitable for medium to hard materials
4. Roll Crusher
Overview:
Roll crushers use friction between rotating rolls to draw material into the crushing zone. Depending on the roll surface, they can crush by compression or splitting.
Aplicaciones:
- Suitable for coal, limestone, clinker, feldspar, and other medium-hard or softer materials.
- Available in single-roll, double-roll, or multi-roll designs.
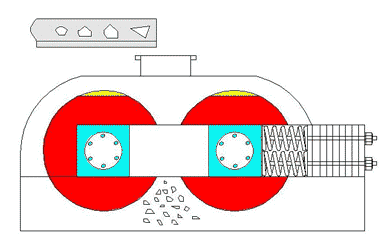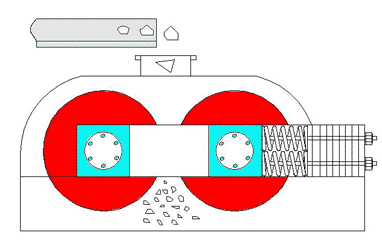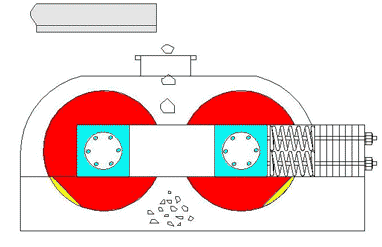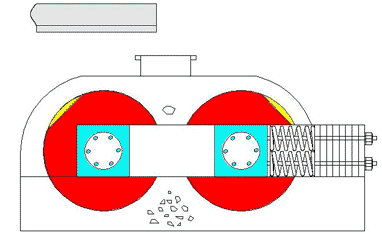
5. Hammer Crusher
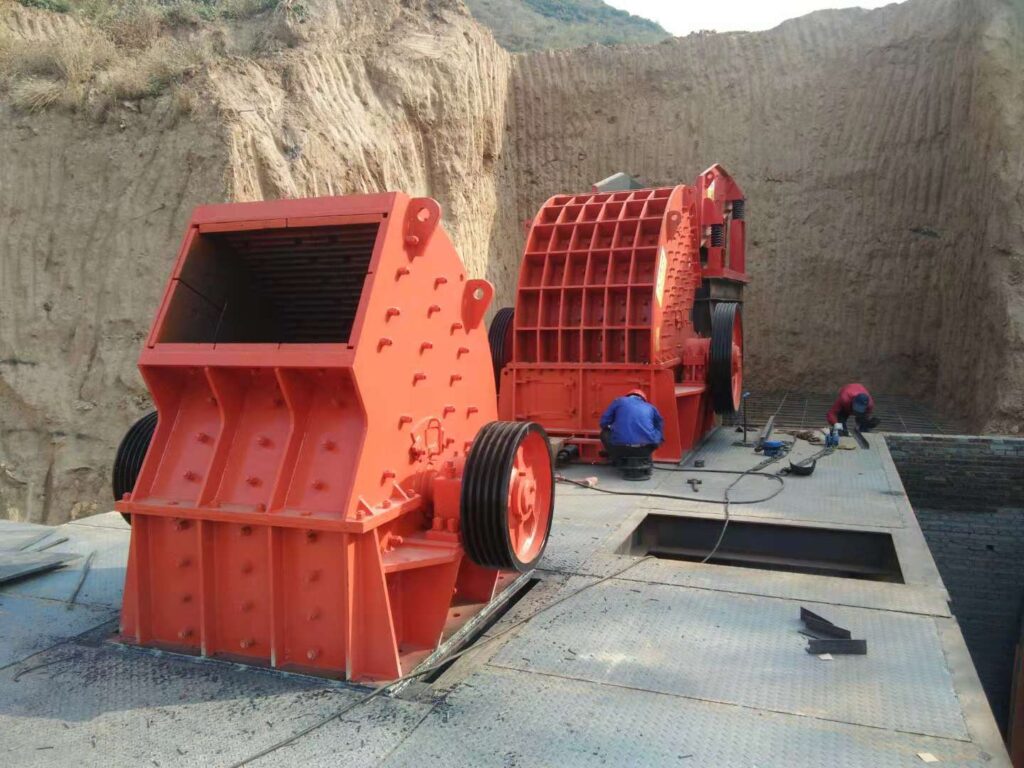
Overview:
Hammer crushers use high-speed hammers to impact and break materials. They are designed for medium and fine crushing of brittle materials.
Principio de trabajo:
Material is struck by a hammer attached to a fast-rotating rotor, then thrown against a breaker plate. The final particle size is controlled by a grate at the bottom of the crusher.
Advantages:
- Large crushing ratio
- Uniform output size
- Bajo consumo de energía
Limitations:
- Not suitable for high-moisture or clay-rich materials
- Higher wear rate of hammers on hard materials

6. Impact Crusher
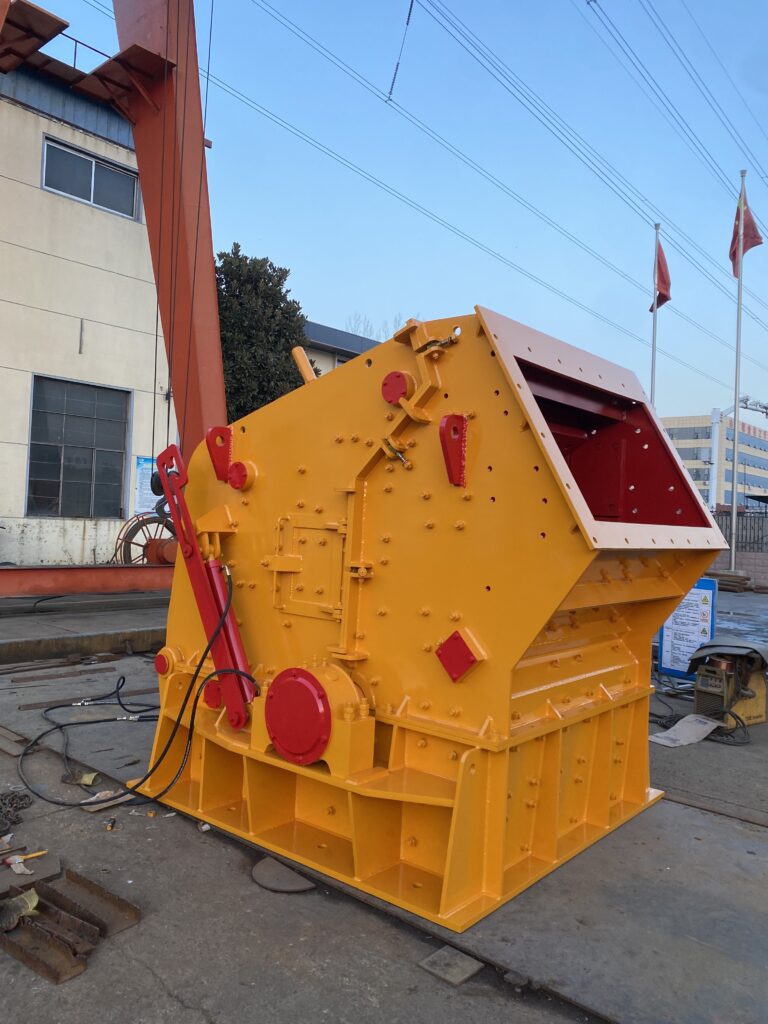
Overview:
Impact crushers rely on high-speed rotors and plate hammers to crush materials. The repeated collisions between the material, hammer, and impact plates result in effective size reduction.
Advantages:
- Higher crushing ratio than hammer crushers
- Efficient use of rotor energy
- Ideal for medium-hard, brittle materials like limestone, coal, dolomite, and gypsum
Limitations:
- Wear-prone plate hammers
- Less suitable for very hard materials

Conclusion
When considering what are the common types of crushing machines, the choice depends on the hardness of the material, the required particle size, and the production capacity needed.
- Jaw Crushers and Gyratory Crushers are best for primary crushing of large feed sizes.
- Cone Crushers and Impact Crushers excel at medium and fine crushing.
- Roll Crushers and Hammer Crushers are suitable for softer, brittle materials.
Selecting the right crusher not only ensures higher efficiency but also reduces maintenance costs and downtime, improving overall production performance.